
- #Logstash filebeats config how to#
- #Logstash filebeats config install#
- #Logstash filebeats config update#
- #Logstash filebeats config free#
The location of these files again may change based on how you installed Logstash and your OS. There are 2 main files to consider one in /etc/logstash/logstash.yml and the other etc/logstash/pipelines.yml. Like Elasticsearch it has a few YAML files to be changed. That mainly covers the Filebeat Aspect of it. You can enable any output location, multiple even as per your requirement. These include Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana, but they would be disabled by default with # signs. Here we can mention where to send our data, most of the popularly used output paths would be written in by default. Moving on the next significant part would be the output section output.logstash: hosts: So we can mention the type of data to be extracted, the path of the files to extract data from, any additional fields that we like to add to the data extracted, any files to exclude, and most importantly the enabled field which describes whether we wish to use that input when we start our Filebeat instance. So first we see the filebeat.inputs each input corresponds to an input location to extract data from. But I’ll dive into some of the more important ones for the purpose of this tutorial filebeat.inputs: - type: log paths: - /var/log/number.log enabled: true The sample YAML file describes most things in detail. This file would contain all the configurations for our file beats process.
#Logstash filebeats config install#
It may change according to your OS and how you chose to install Filebeat if you can’t find it in this directory refer to the guide for your own OS/ Installation method. The Filebeat configuration file is located /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml. First, let’s stop the processes by issuing the following commands $ sudo systemctl stop filebeat $ sudo systemctl stop logstash
#Logstash filebeats config how to#
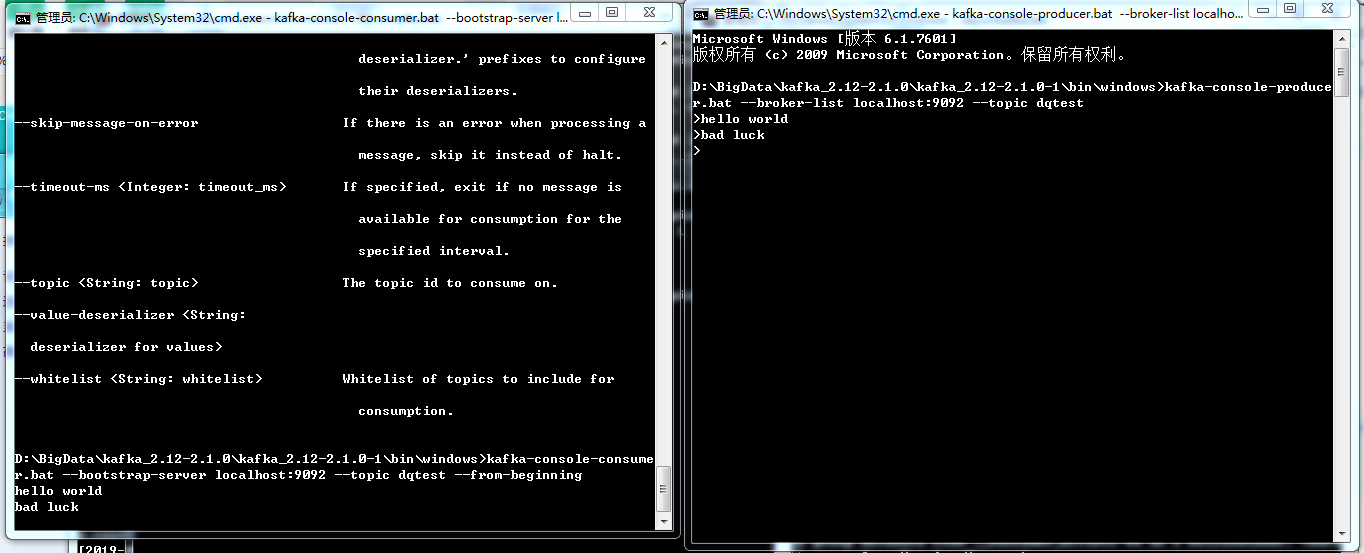
Now that both of them are up and running let’s look into how to configure the two to start extracting logs. You can issue a similar command to startup Filebeat $ sudo systemctl start filebeat $ sudo systemctl status filebeat rvice - Filebeat sends log files to Logstash or directly to Elastic Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rvice disabled vendor preset Active: active (running) since Fri 21:41:07 +0530 22s ago Docs: Main PID: 27548 (filebeat) Tasks: 13 (limit: 4491) CGroup: /system.slice/rvice └─27548 /usr/share/filebeat/bin/filebeat -environment systemd -c /etc Configuring Logstash and Filebeat
rvice - logstash Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/rvice enabled vendor preset: Active: active (running) since Fri 21:34:50 +0530 4s ago Main PID: 26392 (java) Tasks: 17 (limit: 4491) CGroup: /system.slice/rvice └─26392 /usr/bin/java -Xms1g -Xmx1g -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:CMSIn.Seems like it’s inactive we can fix that by starting the service up $ sudo systemctl enable logstash $ sudo systemctl start logstash $ sudo systemctl status logstash Now both Logstash and Filebeat should be installed on your computer Making sure everything is workingįirst, let’s check whether our Logstash is running $ sudo systemctl status logstash rvice - logstash Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/rvice disabled vendor preset Active: inactive (dead) The apt-get command comes to the rescue again as all we have to do is to run a few commands $ sudo apt-get install logstash $ sudo apt-get install filebeat Now since that’s done we can start installing Filebeat and Logstash. You should get the following output openjdk version "1.8.0_242" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_242-b09) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.242-b09, mixed mode)
#Logstash filebeats config update#
As I’m working on a Linux Distro so I can install it using an apt-get command as follows $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdkĪfter you have installed it issue the following command $ java -version For those of you who do not have the JDK version installed, you can install it with a few commands.
#Logstash filebeats config free#
If you already have a compatible JDK version installed feel free to skip this part of the tutorial. You can check your required Java JDK version for your version of Logstash by referring to the dependency matrix mentioned here. As of writing this article the latest version of Logstash is v7.8 which works with OpenJDK v1.8. First, we need to find out the JDK version required. So let’s start at the beginning with Filebeat and Logstash Installing Filebeat and Logstashīefore we begin we need to ensure we have a proper Java JDK installed. Now we are going to dive into implementing the Elastic Stack. In the last article, I gave you a brief introduction to Elastic Stack.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
